CSR: Moral duty or obligation
Corporate social responsibility is commitment of an organization to fulfill the expectations of their stakeholders in addition to maintaining the sustainability of environment. To understand the concept of corporate social responsibility better, we have to understand the stakeholders first.
Stakeholders are persons, groups, government agencies and other institutions directly affected by the decisions of the organization and that hold a stake in its performance. Stakeholders group include shareholders, customers, employees, suppliers, community members and government representatives and regulators who regulates and makes rules and regulations for the organizations. The network of stakeholders can be easily understood with the help of following figure.
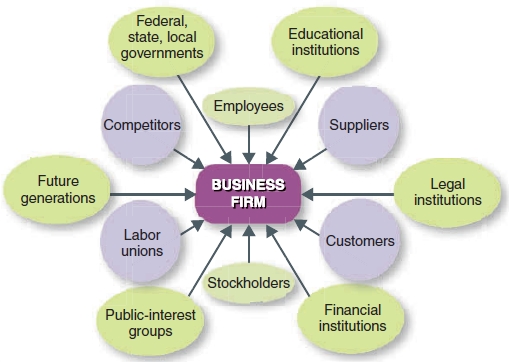
Image source: Schermerhorn, J.R., 2013. Ethics And Social Responsibility. 12e, Management LearnISucceed, p.73.
Corporate social responsibility is the obligation toward society assumed by business. Corporate social responsibility reflects the social imperatives and the social consequences of business success and consists broadly of policies and practices that reflect business responsibility for some of the wider societal good. CSR actions and policies take into account stakeholders’ expectations and often consider the triple bottom line of economic, social, and environmental performance. The precise policies and practices underlying this responsibility lie at the discretion of the corporation. Some companies refer to their CSR practices in terms of sustainability, on the grounds that these efforts maintain positive long-term relationships with communities, employees, customers, governments, and the natural environment.
Social responsibilities can be categorized into four categories as shown in following figure:

Image Source: Bateman, T. and Snell, S., 2012. M: Management. McGraw-Hill Higher Education. Pg. 169
The economic responsibilities of business are to produce goods and services that society wants at a price that perpetuates the business and satisfies its obligations to investors. For Smithfield Foods, the largest pork producer in the United States, this means selling bacon, ham, and other products to customers at prices that maximize Smithfield’s profits and keep the company growing over the long term. Economic responsibility may also extend to offering certain products to needy consumers at a reduced price.
Legal responsibilities are to obey local, state, federal, and relevant international laws. Laws affecting Smithfield cover a wide range of requirements, from filing tax returns to meeting worker safety standards.
Ethical responsibilities include meeting other societal expectations, not written as law.
Finally, philanthropic responsibilities are additional behaviors and activities that society finds desirable and that the values of the business support. Examples include supporting community projects and making charitable contributions. Philanthropic activities can be more than mere altruism; managed properly, strategic philanthropy can become not an oxymoron but a way to build goodwill in a variety of stakeholders and even add to shareholder wealth.
Difference between Moral duty and obligation: Moral duty is that type of responsibility whose fulfillment totally depends on moral values and ethics of the individual or organization. In the case of moral duty, it is the organization who has right to make the final decision without any obligation and no any legal action can be taken against him but it should not harm the welfare of stakeholders in any way. When the organizations don’t want to fulfill their duties and try to dodge their responsibilities then government regularities and agencies have to interfere and take some legal actions. In the situation of interference by government agencies moral duty doesn’t remain moral duty and becomes obligation for the organizations and they are obliged by law fulfill their responsibilities in any way.
The difference between moral duty and obligation can be understood easily by analyzing the history of CSR where product safety, employees’ safety & privacy and sustainability of natural resources were moral duties of organizations but they failed to perform their duty.
Social Responsibility as moral duty: Moral duty of an individual or organization fully depends on their moral values as they are not obliged to perform that. In present time the situation is very difficult as corona virus (COVID-19) is spreading all over the world and WHO has declared it as pandemic. Most of the countries that are fighting with COVID-19 finding out that their resources are not sufficient to defeat this disease, even developed countries like U.S.A., Italy and Spain are running out of resources while fighting with this virus. In this critical situation many organizations like Amazon, Microsoft and Alibaba are coming forward to help their governments by making some financial donations and useful resources. Moral duty can be understood easily with this incident as few companies are doing more than their potential to fight with this pandemic while other organizations are doing nothing, another important thing is that no one force these organizations to do something as this is their moral duty and they are not obliged to perform that.
Social Responsibility as obligation: Clearly, a business firm has a responsibility to its stakeholders to make profits in order to maximize the value of their investment and to improve the firm’s growth potential. It is also clear that businesses need to obey the laws relating to the overall conduct of doing business, such as operating within the rules of competition laws, honoring contracts with business partners (suppliers, distributors, franchisers, etc). Less obvious, but equally important, are the responsibilities that businesses have relating to employer-employee relations in areas such as pensions and other benefits, employment conditions, health and safety at the place of work, sex and racial discrimination, social exclusion, etc. The organizations are also responsible to maintain the safety and privacy of their customers as well as employees’ safety and privacy also. In the condition of negligence to fulfill these responsibilities the government has to interfere and make these responsibilities as obligation for the organizations and this is necessary for the welfare of society.
In last, it can be concluded that the organizations should perform their duty and fulfill their responsibility whether it is legal or ethical. There is no any doubt that an organization’s primary responsibility is to make profit for their shareholders but no any corporation should run their business in the market with an aim of profit making only, they are obliged to take the responsibility of society in crisis like COVID-19.
Author –
Pankaj Gautam
Program Coordinator(BBM)
LBEF Campus